
The Limitations of Traditional Note-Taking Methods
linear note-taking, while familiar, has several drawbacks:
Difficulty connecting related concepts
Challenges in quickly finding specific information
Limited ability to see the big picture
Missed opportunity to grasp overarching themes
Inability to visualize relationships between topics
In today's information-rich world, we need more effective methods of knowledge management. The importance of retaining and applying complex information is crucial, especially in academic and professional settings where deep understanding and innovative thinking are valued.
Mind Mapping: A Visual Alternative to Linear Notes
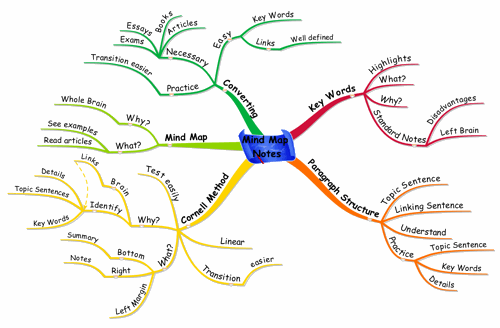
Mind mapping is a powerful visual technique that offers a refreshing alternative to traditional linear note-taking. It involves creating a diagram that represents ideas, tasks, or concepts linked to and arranged radially around a central theme.
Benefits of mind mapping for information retention include:
Enhanced memory recall through visual associations
Improved understanding of complex topics
Easier identification of connections between ideas
Sparks creativity and helps in problem-solving
Reveals patterns or links not apparent in linear formats
The Cornell Method: Structured Non-Linear Note-Taking
The cornell method offers a structured approach to note-taking that combines elements of both linear and non-linear systems. It involves dividing a page into three sections: a narrow left column for cues, a wider right column for notes, and a bottom section for summarizing.
This method provides significant advantages for both students and professionals:
Organized format for easy review and retention
Built-in study guide through the cue column
Promotion of active engagement with the material
Facilitation of creating study guides and summaries
Easy sharing of information with colleagues or classmates
Digital Tools for Non-Linear Note-Taking
Popular note-taking apps offer robust features for non-linear note-taking:
Feature | Evernote | Notion | OneNote |
|---|---|---|---|
Organization | Notebooks and tags | Databases and linked pages | Notebooks, sections, and pages |
Search | Powerful, includes text in images | Comprehensive, with filters | Full-text search, including handwriting |
Collaboration | Shared notebooks | Real-time collaboration | Shared notebooks |
Integration | Wide range of app integrations | API for custom integrations | Strong Microsoft ecosystem integration |
AI-Powered Knowledge Mapping with Ponder
Ponder leverages artificial intelligence to revolutionize how we interact with complex information. It converts documents into interactive knowledge maps, performs deep analysis of content to identify key concepts and relationships, and creates visual representations of document knowledge structures.
Ponder addresses many pain points associated with traditional note-taking methods by enabling rapid grasp of key ideas from complex documents, effortless multi-document comparison, and AI-powered insights and connections between concepts. It has the potential to spark new ideas and research directions, transforming note-taking into an active, AI-assisted exploration of knowledge.
Sketchnoting: Combining Visuals and Text
Sketchnoting is a creative note-taking method that combines text, images, and structure to create visually appealing and informative notes. This technique engages both the visual and verbal processing centers of the brain, potentially leading to better retention and understanding of information.
Tips for effective sketchnoting:
Start with basic shapes and icons
Use varying text sizes to indicate importance
Incorporate color to categorize or emphasize information
Practice common visual elements like arrows, boxes, and dividers
Focus on key concepts rather than trying to capture everything
The Charting Method: Organizing Information in Tables
The charting method involves organizing information into tables or charts, making it particularly useful for comparing and contrasting ideas or summarizing large amounts of information. This method is especially beneficial for subjects with many facts, figures, or relationships between concepts.
The charting method is particularly effective for:
Comparing and contrasting multiple ideas or theories
Organizing historical events or timelines
Summarizing scientific data or research findings
Tracking project progress or milestones
Analyzing literary works or characters
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Note-Taking Method for You
Selecting the most effective note-taking method depends on your personal learning style, the subject matter, and the context in which you're taking notes. Experiment with different techniques to find what works best for you. Remember, the goal is not just to record information, but to engage with it in a way that enhances understanding and retention.
By leveraging these alternative note-taking methods and tools, you can enhance your information retention, improve your understanding of complex topics, and streamline your knowledge management process. Whether you choose mind mapping, the Cornell Method, digital tools, or AI-powered solutions like Ponder, moving beyond linear note-taking can significantly boost your learning and productivity.
