
Have you ever stared at a complicated knowledge map or diagram and felt completely overwhelmed? Those interconnected bubbles and lines might look impressive, but they can quickly become a tangled mess that's harder to understand than the original information. As someone who's spent years helping researchers make sense of complex data, I've seen this frustration firsthand.
Node-based representations are powerful tools for organizing information - but only when you can actually use them effectively. The good news? There are proven strategies to transform those complicated webs into clear, intuitive knowledge structures.
In this guide, I'll share five practical tips to simplify even the most complex node-based systems, making your research process significantly more efficient.
Understanding Node-based Representations in Modern Knowledge Work
What Exactly is a Node-based Representation?
At its core, a node-based representation is a visual way to organize information using connected points (nodes) and relationships (edges). Think of it like a map of ideas where each concept is a point, and the lines between them show how they relate.
These structures appear everywhere from mind maps and concept diagrams to knowledge graphs and research frameworks. They're especially valuable for visualizing complex relationships that might get lost in traditional linear documents.
Common Applications of Node-based Systems
Node-based representations appear across numerous domains:
Academic research to map relationships between theories and findings
Business analytics to visualize data connections and insights
Software development to model system architecture
Project management to organize task dependencies
Learning and education to structure complex topics
Why Node-based Representations Matter for Research and Learning
For anyone engaged in deep research or knowledge work, node-based systems offer distinct advantages over linear text. They allow you to:
See relationships between ideas at a glance
Identify patterns that might remain hidden in traditional documents
Build more holistic understanding of complex topics
Navigate information non-linearly based on your interests
Update and expand your knowledge structure organically
However, these benefits quickly diminish when node systems become too complex - which brings us to our next point.
The Challenges of Working with Complex Node Structures
Information Overload in Node Diagrams
The most common complaint I hear from researchers is simply: "There's too much going on!" When a knowledge map contains dozens or hundreds of nodes, the cognitive load becomes overwhelming. Your brain can only process a limited amount of visual information at once, and exceeding that threshold makes the entire representation less useful.
Difficulty Tracking Relationships Between Nodes
Even with a reasonable number of nodes, tracking all the connections between them becomes exponentially more difficult as complexity increases. Important relationships get buried in visual noise, defeating the purpose of the representation.
Time-consuming Analysis of Node-based Data Structures
Creating and maintaining detailed node structures manually requires significant time investment. Researchers often find themselves spending more time organizing their visual knowledge system than actually generating insights from it.
The Learning Curve for Non-technical Users
For those without technical backgrounds, node-based systems can feel intimidating. The specialized vocabulary and abstract nature of node representations create barriers to adoption, especially for newcomers to a research topic.
Now let's explore practical solutions to these challenges.
Tip #1: Master Node Hierarchy Organization for Clearer Representation
Establishing Logical Node Classification Systems
The foundation of any effective node representation is a clear classification system. Before you dive into creating complex connections, establish:
A consistent node taxonomy (what types of nodes exist in your system)
Visual distinctions between different node categories
Clear rules for how nodes relate to one another
For example, if you're mapping research on climate change, you might categorize nodes as "empirical studies," "theoretical frameworks," "policy recommendations," and "critique points."
Techniques for Grouping Related Nodes
Rather than displaying all nodes equally, create visual clusters that reflect natural groupings in your information:
Spatial clustering: Position related nodes closer together
Container elements: Place groups of nodes inside visual boundaries
Collapsible sections: Allow sub-topics to be hidden when not needed
How Ponder AI Automatically Organizes Node Hierarchies
This is where AI-powered research tools shine. Ponder automatically analyzes documents to identify natural hierarchies and relationships, organizing nodes into logical groups without manual effort. The system recognizes the inherent structure in academic papers and other complex documents, creating hierarchical node arrangements that make intuitive sense.
Tip #2: Implement Visual Simplification for Node-based Diagrams
Strategic Color-coding for Node Types
Colors are powerful cognitive shortcuts. A thoughtful color system allows you to:
Instantly recognize different node types
Identify the most important nodes at a glance
Trace related concepts across a complex diagram
Stick to a limited palette of 5-7 colors maximum to avoid creating new visual complexity.

Size and Prominence Adjustments for Critical Nodes
Not all nodes deserve equal visual weight. Make your most important concepts larger and more prominent, while keeping supporting information visually subordinate. This creates natural pathways for navigating the representation.
How Ponder Transforms Complex Papers into Visual Knowledge Maps
With Ponder, you don't need to manually design these visual elements. The AI analyzes the semantic importance of different concepts in your research materials and automatically creates visually optimized knowledge maps. The one-click PDF upload feature transforms dense academic papers into structured node representations where the most significant concepts naturally stand out.
Tip #3: Utilize Node Filtering and Progressive Disclosure Techniques
When and How to Filter Non-essential Nodes
Even the most well-organized node system benefits from selective filtering. Consider:
Creating simplified views that show only high-level concepts
Filtering nodes by category, importance, or relevance to current focus
Temporarily hiding nodes that aren't relevant to your current question
These approaches reduce cognitive load while maintaining access to your complete knowledge structure.
Creating Expandable Node Sections for Detailed Exploration
Progressive disclosure - revealing information only when needed - is crucial for complex node systems. Design your representations so users can:
Start with a high-level overview
Click or expand sections to reveal greater detail
Navigate deeper into specific areas of interest
This approach makes even the most complex node structures accessible.
Ponder's Approach to Flexible Knowledge Organization
Ponder's digital canvas implements progressive disclosure by design. The system presents an intuitive overview of research material while allowing you to expand any node to explore supporting evidence, contradictory viewpoints, or related concepts. This flexible approach maintains clarity regardless of how deep you want to explore.
Tip #4: Create Interactive Node Navigation Systems
The Advantages of Dynamic vs. Static Node Representations
Static node diagrams quickly become limiting. Interactive, dynamic representations allow:
Zooming between different levels of detail
Rearranging nodes based on changing focus
Searching and jumping directly to relevant nodes
Highlighting paths and relationships on demand
Building Intuitive Node Navigation Experiences
Effective node navigation requires thoughtful user experience design:
Clear visual cues indicating what's clickable
Consistent interaction patterns
Smooth transitions between different views
Easy ways to backtrack or return to overview
How Ponder Enables Interactive Knowledge Map Exploration
Ponder's thinking workspace provides an intuitive navigation system for complex knowledge structures. The interface allows seamless movement between broad conceptual frameworks and specific details, making it easy to follow your natural research curiosity while maintaining context.
Tip #5: Leverage AI for Node Analysis and Pattern Recognition
Using AI to Identify Meaningful Node Connections
Modern AI can analyze node relationships to reveal non-obvious connections. This capability helps:
Discover unexpected relationships between concepts
Identify clusters and patterns automatically
Suggest new areas for exploration based on existing knowledge
Automating Insight Extraction from Node Relationships
Beyond just showing relationships, AI can help extract actionable insights:
Identifying contradictions or gaps in knowledge
Highlighting the strongest evidence paths
Summarizing complex node clusters into accessible insights
Ponder's AI Technology Trained on 200M+ Academic Papers
Ponder's AI has been trained on over 200 million academic papers, giving it unprecedented ability to understand and organize complex knowledge. This powerful foundation allows it to identify meaningful patterns in your research that might otherwise remain hidden, transforming raw information into structured, actionable knowledge.
Transforming Your Research with Node-based Knowledge Representation
One-click Conversion from Documents to Knowledge Maps
With Ponder, transforming linear documents into rich node-based representations requires just a single click. Upload a PDF, and the system automatically extracts key concepts, establishes relationships, and creates an interactive knowledge map that makes complex information accessible.
Multi-document Comparison for Enhanced Node Analysis
One of the most powerful applications of node-based systems is comparing information across multiple sources. Ponder excels here, allowing you to visualize similarities, contradictions, and complementary information across different research papers in a unified node representation.
Building Permanent Knowledge Structures with Node-based Systems
Unlike traditional AI chatbots that provide temporary, linear answers, Ponder's node-based approach creates permanent knowledge structures you can revisit, expand, and refine over time. This builds a lasting research asset rather than ephemeral information snippets.
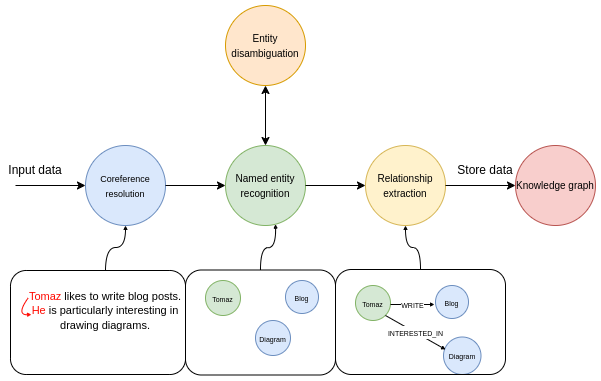
Conclusion: The Future of Node-based Representation in Research
Recap of Simplification Strategies
We've explored five key strategies for making complex node-based representations more accessible:
Establishing clear node hierarchies and classifications
Implementing thoughtful visual design principles
Using progressive disclosure and filtering techniques
Creating interactive navigation systems
Leveraging AI for pattern recognition and insight extraction
How AI is Revolutionizing Node-based Knowledge Work
We're entering a new era where AI doesn't just process information but helps us organize and understand it. By combining human intuition with AI-powered knowledge mapping, researchers can navigate complexity more effectively than ever before.
Getting Started with Ponder for Advanced Node Representation
Ready to transform how you work with complex information? Ponder's AI-powered research workspace makes node-based knowledge representation accessible to everyone from students to advanced researchers. The system combines search, reading, note-taking, and questioning in an integrated workflow that turns information overload into clear, actionable insights.
By implementing these strategies and leveraging the right tools, you can master even the most complex node-based representations - turning information chaos into structured knowledge that drives your research forward.